技巧 8:Few-Shot Chain of Thought
要解決這個缺陷,就要使用到新的技巧,Few-Shot Chain of Thought。
根據 Wei 他們團隊在 2022 年的研究表明:
透過向大語言模型展示一些少量的範例,並在範例中解釋推理過程,大語言模型在回答提示時也會顯示推理過程。這種推理的解釋往往會引導出更準確的結果。
下面是論文裡的案例,使用方法很簡單,在技巧 2 的基礎上,再將邏輯過程告知給模型即可。從下面這個案例裡,你可以看到加入解釋後,輸出的結果就正確了。
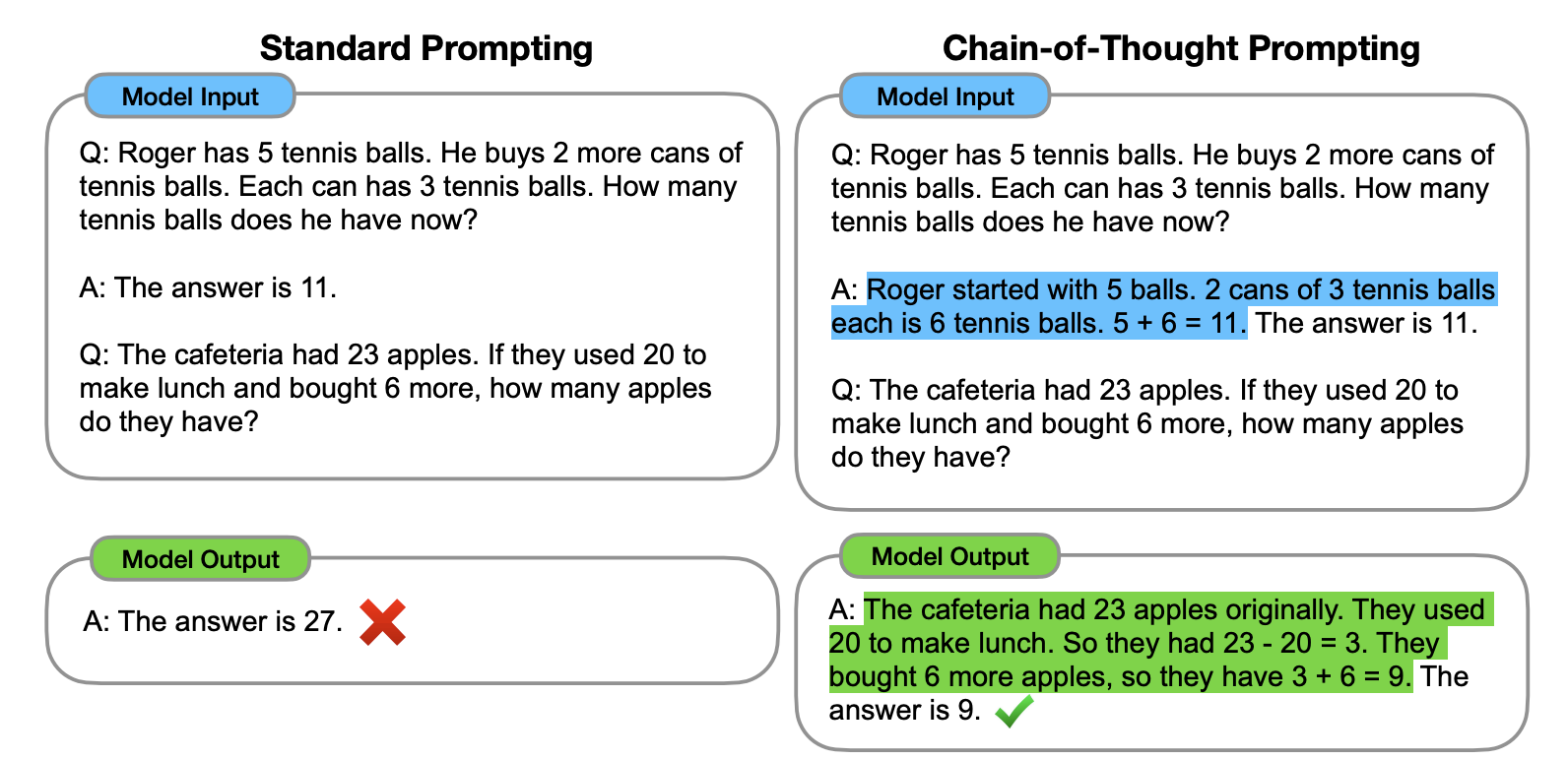
那本章開頭提的例子就應該是這樣的(注:本例子同樣來自 Wei 團隊論文):
The odd numbers in this group add up to an even number: 4, 8, 9, 15, 12, 2, 1.
A: Adding all the odd numbers (9, 15, 1) gives 25. The answer is False.
The odd numbers in this group add up to an even number: 17, 10, 19, 4, 8, 12, 24.
A: Adding all the odd numbers (17, 19) gives 36. The answer is True.
The odd numbers in this group add up to an even number: 16, 11, 14, 4, 8, 13, 24.
A: Adding all the odd numbers (11, 13) gives 24. The answer is True.
The odd numbers in this group add up to an even number: 17, 9, 10, 12, 13, 4, 2.
A: Adding all the odd numbers (17, 9, 13) gives 39. The answer is False.
The odd numbers in this group add up to an even number: 15, 32, 5, 13, 82, 7, 1.
A:
聊完技巧,我們再結合前面的 Zero-Shot Chain of Thought,來聊聊 Chain of Thought 的關鍵知識。根據 Sewon Min 等人在 2022 年的研究 表明,思維鏈有以下特點:
- "the label space and the distribution of the input text specified by the demonstrations are both key (regardless of whether the labels are correct for individual inputs)" 標籤空間和輸入文字的分佈都是關鍵因素(無論這些標籤是否正確)。
- the format you use also plays a key role in performance, even if you just use random labels, this is much better than no labels at all. 即使只是使用隨機標籤,使用適當的格式也能提高效能。
理解起來有點難,我一個 prompt 案例給大家解釋(🆘 如果你有更好的解釋,不妨反饋給我)。我給 ChatGPT 一些不一定準確的例子:
I loved the new Batman movie! // Negative
This is bad // Positive
This is good // Negative
What a good show! //
Output 是這樣的:
Positive
在上述的案例裡,每一行,我都寫了一句話和一個情感詞,並用 // 分開,但我給這些句子都標記了錯誤的答案,比如第一句其實應該是 Positive 才對。但:
- 即使我給內容打的標籤是錯誤的(比如第一句話,其實應該是 Positive),對於模型來說,它仍然會知道需要輸出什麼東西。換句話說,模型知道 // 劃線後要輸出一個衡量該句子表達何種感情的詞(Positive or Negative)。這就是前面論文裡 #1 提到的,即使我給的標籤是錯誤的,或者換句話說,是否基於事實,並不重要。標籤和輸入的文字,以及格式才是關鍵因素。
- 只要給了範例,即使隨機的標籤,對於模型生成結果來說,都是有幫助的。這就是前面論文裡 #2 提到的內容。
最後,需要記住,思維鏈僅在使用大於等於 100B 引數的模型時,才會生效。
BTW,如果你想要瞭解更多相關訊息,可以看看斯坦福大學的講義:Natural Language Processing with Deep Learning